What is Business Analysis?
Business analysis is a well-curated actionable method(s) of identifying business needs and finding solutions to business problems. Solutions could include anything from upgrading software-systems to process improvement, organizational change or development of new policies. The person charged with the responsibility of carrying out this task is called a Business Analyst. It is used to identify and affect the need for change in how organizations operate.
Who is a Business Analyst?
A business analyst is a person responsible for identifying and defining business problems that will maximize the quality of the organization’s output. The business analyst role cuts across every level of the organization as they seek to proffer the best solutions to problems as it affects the individual unit.
How To Conduct A Business Analysis Process
Before the company embarks on any project or makes an investment decision, it is essential to start with business analysis. The business analysis process is broadly divided into several steps. Each of these steps involves tasks to perform, laid down principles and documents to produce. The frequency and order of occurrence are not static, it usually depends on the project.
The following are steps to conducting a business analysis
- Collect Background Information
- Know who the Stakeholders are.
- Identify the Business Objectives
- Evaluate your options
- Determine the project requirements
- Define the scope of operation.
- Business Analysis Plan
- Initial implementation through sampling
Business Analysis Techniques
Business analysis has taken a significant turn in the last few years with the creative approaches of best business analysis techniques. The main objective of these techniques is to get the best results as a business solution. Here are some of the most sought after business analysis techniques;
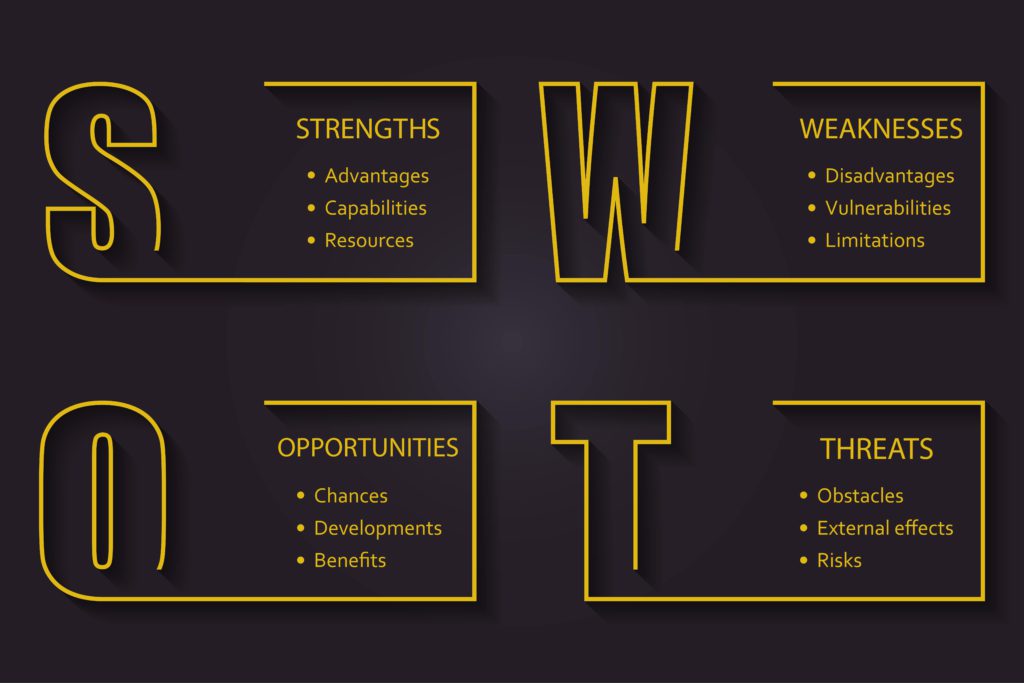
1. SWOT Analysis
The term SWOT stands for its four elements–
- S- Strength
- W- Weakness
- O- Opportunities
- T- Threats
The SWOT analysis is a fundamental tool in a Business Analysis machine. It identifies a business’s strengths and weaknesses and evaluates opportunities or threats that are imminent to the company. The goal is to maximize the value of the organization’s strength and opportunities while bracing for the impact of the threats and weakness.
As a result, stakeholders can make strategic decisions regarding their business based on the outcome of the SWOT analysis. Furthermore, SWOT analysis is relatively straightforward. A typical SWOT model will have four quadrants of each SWOT component. With each of the quadrant highlighting the individual results.
2. PESTLE Analysis
There are always environmental factors which impact business planning. The term PESTLE stands for:
- P- Political
- E – Economic
- S – Social
- T – Technological
- L- Legal
- E – Environmental
Each of the factors mentioned above has influences in making a business decision final. Hence, analyzing such key drivers is an essential task of a business analyst.
A PESTLE analysis often works alongside SWOT analysis. It evaluates external factors that could impact business performance. This acronym stands for six elements affecting business: political, economic, technological, environmental, legal, and sociological.
It also assesses the various factors within each component, as well as their potential effect and the kind of impact (i.e., negative or positive) on the government.
This type of business analysis helps stakeholders evaluate the organization’s risk exposure and review business objectives. As a result, giving the organization an advantage over competitors
3. MOST Analysis
The term MOST stands for four components, namely –
- M-Mission
- O-Objective
- S-Strategy
- T-Tactics
The MOST analysis is a standard business analysis model and one of the best business analysis techniques. The business analysts evaluate what an organization does and plans to achieve in the near or distant future.
Hence, it is a clear way to understand an organization on its potential and business resolutions.
4. CATWOE Analysis
CATWOE is an acronym for
- Clients
- Actors
- Transformation
- Weltanschauung or World View
- Owner
- Environmental Constraints
CATWOE is a general thought process of business analysis to understand what the organization is trying to achieve. It carefully pinpoints what the problem areas are and how the solution will affect the business and its associated people.
5. Process flow diagram
A process flow diagram (PFD) is commonly used in manufacturing, chemical and process engineering to identify the flow of plant processes. Also, it can be used in other sectors to help stakeholders understand how their business operates.
A PFD is best used to:
- Document a flow of a process.
- Study the process to make replacements and improvements.
- Improve understanding and communication channels between stakeholders.
Conclusion
However, it is essential to note that not all the best business analysis techniques are used throughout a project. It could be applicable for a specific cycle of a project like at the beginning or at the end of the project.
In addition, not all the best business analysis techniques apply to all projects. Some are tailored to a specific project and used for particular purposes.
Lastly, a business analysis should not be confused with a business strategy.
